Anil Kakkar/TNF
The Himalayas, often referred to as the “Roof of the World,” are not just a breathtaking marvel of nature but also a vital life-support system for millions of people across Asia. However, this majestic mountain range is increasingly becoming a hotspot for natural crises, threatening both the environment and human life. From landslides and glacial melt to flash floods and earthquakes, the Himalayas are under siege, and the reasons behind this escalating crisis are deeply intertwined with human activity and climate change. This article explores the causes of the Himalayan crisis, the risks it poses to humanity, and potential solutions to safeguard this fragile region.
The Causes Behind the Himalayan Crisis
- Climate Change and Global Warming:
The Himalayas are particularly vulnerable to the impacts of climate change. Rising global temperatures have accelerated the melting of glaciers, which are the primary source of water for major rivers like the Ganges, Indus, and Brahmaputra. This glacial melt not only disrupts the natural flow of these rivers but also contributes to the formation of glacial lakes, which are prone to catastrophic outbursts. Moreover, warmer temperatures have altered precipitation patterns, leading to more intense and erratic monsoon rains, which exacerbate the risk of landslides and flash floods. - Deforestation and Unsustainable Development:
Rapid deforestation in the Himalayan region, driven by logging, agriculture, and infrastructure development, has severely compromised the stability of the slopes. Trees play a crucial role in binding the soil and regulating water flow, and their removal leaves the land vulnerable to erosion and landslides. Additionally, the construction of roads, dams, and buildings without proper environmental assessments has further destabilized the fragile ecosystem, making it more susceptible to natural disasters. - Population Pressure and Over exploitation:
The growing population in the Himalayan region has led to the over exploitation of natural resources. Unsustainable farming practices, overgrazing, and the extraction of minerals have degraded the land and depleted water sources. The increasing demand for land and resources has pushed human settlements into hazard-prone areas, heightening the risk of natural disasters. - Seismic Activity:
The Himalayas are located in a tectonically active zone, where the Indian plate collides with the Eurasian plate. This makes the region highly prone to earthquakes, which can trigger landslides and avalanches. The combination of natural seismic activity with human-induced environmental degradation has amplified the frequency and severity of disasters in the region.
The Great Risks for Humans
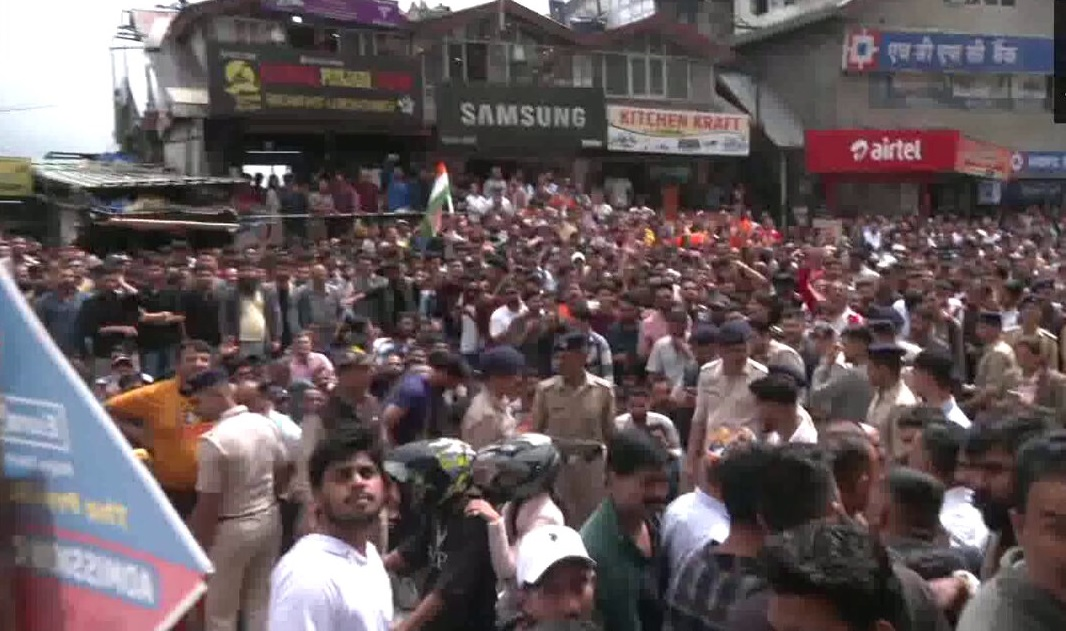
The natural crises in the Himalayas pose significant risks to human life and livelihoods. The frequent occurrence of landslides and flash floods can result in loss of life, destruction of property, and displacement of communities. The melting glaciers threaten to disrupt the water supply for millions of people downstream, leading to water scarcity and affecting agriculture, which is the primary source of livelihood for many Himalayan communities. Moreover, the increased risk of earthquakes and other seismic events poses a constant threat to the safety of those living in the region.
Solutions to Safeguard the Himalayas
- Sustainable Development Practices:
It is crucial to adopt sustainable development practices that prioritize the conservation of the environment. This includes implementing stricter regulations on deforestation, promoting reforestation, and ensuring that infrastructure projects are designed with environmental considerations in mind. Developing eco-friendly tourism and agriculture practices can also help reduce the strain on the region’s natural resources. - Climate Action and Adaptation:
Addressing the root cause of climate change is essential to mitigating its impact on the Himalayas. This requires global efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and transition to renewable energy sources. Additionally, local adaptation strategies, such as building resilient infrastructure, creating early warning systems, and promoting water conservation, can help communities cope with the changing climate. - Disaster Preparedness and Risk Reduction:
Enhancing disaster preparedness and risk reduction measures is critical to minimizing the impact of natural crises in the Himalayas. This includes conducting regular risk assessments, strengthening early warning systems, and improving emergency response capabilities. Educating local communities about disaster risks and involving them in planning and decision-making processes can also enhance their resilience to natural disasters. - Tectonic and Geotechnical Monitoring:
Given the seismic activity in the region, it is important to invest in advanced tectonic and geotechnical monitoring systems. These systems can provide early warnings of potential earthquakes, landslides, and other geological hazards, allowing for timely evacuations and other preventive measures.
The Himalayan crisis is a stark reminder of the delicate balance between nature and human activity. While the challenges are immense, there is still hope to protect this vital region through sustainable practices, climate action, and enhanced disaster preparedness. The future of the Himalayas depends on our ability to recognize the risks, address the causes, and implement effective solutions that safeguard both the environment and the millions of people who depend on it. As we move forward, it is imperative that we treat the Himalayas not just as a natural wonder, but as a fragile giant that requires our utmost care and respect.